Amides .
100 - 3000 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
X
Amides . Price And Quantity
- 1000 Kilograms
- 100 - 3000 INR/Kilograms
Amides . Trade Information
- 100000 Kilograms Per Day
- 5-7 Days
Product Description
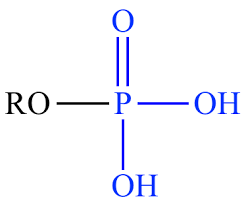
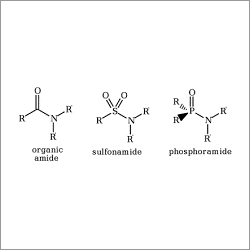
Amides are usually regarded as derivatives of carboxylic acids in which the hydroxyl group has been replaced by an amine or ammonia. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen is delocalized into the carbonyl, thus forming a partial double bond between N and the carbonyl carbon.
Enter Buying Requirement Details